Motivation
面临的挑战: (1) 目前设计只考虑可能调度的一小部分 (2) 使用专用的搜索程序来做关键选择 (3) 使用人工设计的代价模型来探索空间 作者的解决方案
- a new parameterization of the search space
- a more general search algorithm with backtracking and coarse-to-fine refinement
- a new cost model that combines symbolic analysis with machine learning
- a robust methodology which trains the cost model on an infinite population of random programs
- the optional use of sampling and benchmarking to further improve performance given extra time
Navigating the halide scheduling space
Halide 基础概念
- Halide程序由多个stages组成,形成有向无环图(DAG)
- 指定期望的输出区域
- 编译器负责推断需要计算的区域
调度的两个核心选择
Intra-stage order: 决定如何计算一个stage内的所有点(包括维度顺序和平铺选择,可以选择并行化、向量化或展开循环) Cross-stage granularity: 决定何时计算每个stage的结果,以及存储多久(选择在不同粒度级别计算和存储,支持完全计算、内联计算或增量计算等策略)
搜索算法
- 使用基于beam search的算法
- 维护k个候选状态进行搜索
- 使用成本模型对候选进行评估和排序
- 采用粗到细的调度细化策略(使用hash函数控制搜索深度、在高层决策上保持多样性、分多次pass逐步细化调度)
Predicting runtime
Featurizing a Schedule
算法特定特征:
- 计算单个点所需的操作直方图
- 访问其他stage时的Jacobian矩阵
- 用于分类内存访问类型
调度相关特征:
- 事件计数
- 内存占用特征
- 在多个位置分析读写区域的形状
- 使用Halide的边界推断机制进行符号区间分析
Cost Model Design
创新点: 不直接预测运行时间 采用混合方法: 手工设计一些非线性项、使用神经网络预测这些项的系数、最终运行时间是它们的点积 网络架构: 两个输入头(调度特征嵌入、算法特征嵌入)、特点(对调度特征进行对数变换、算法特征权重通过sigmoid保持为正)、输出27个系数用于手工设计的项
Autotuning
通过采样和基准测试改进: 使用成本模型进行重要性采样、以概率p选择最优预测状态、否则尝试次优状态 进一步优化: 对采样结果进行基准测试、使用测试结果重新训练模型、迭代改进预测准确性
### Evaluation
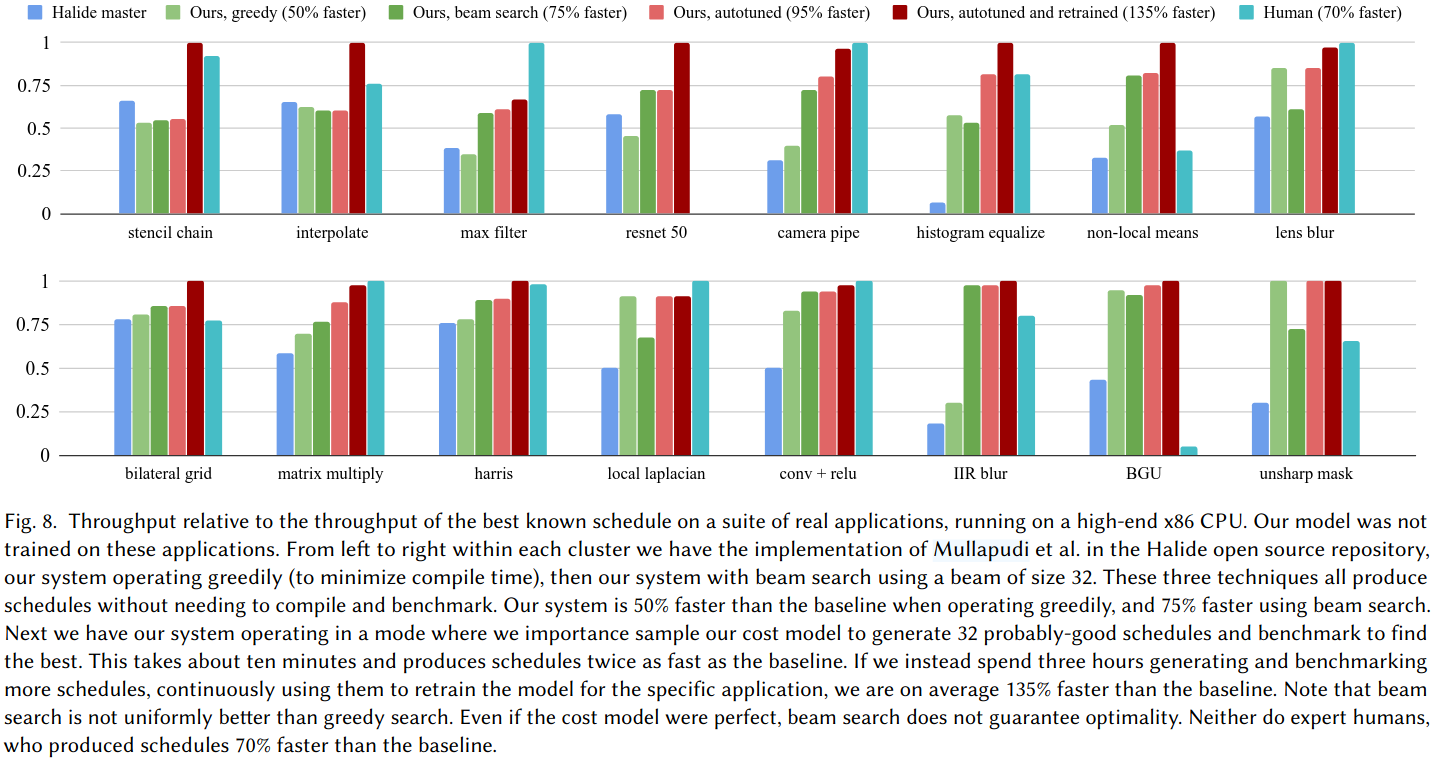
### Reference
Learning to Optimize Halide with Tree Search and Random Programs
FEATURED TAGS
Genetic Algorithm
Multi-objective Optimization
Instruction-Level Parallelism(ILP)
Compiler
Deep Learning Accelerators
Tensor Compiler
Compiler Optimization
Code Generation
Heterogeneous Systems
Operator Fusion
Deep Neural Network
Recursive Tensor Execution
Deep Learning
Classical Machine Learning
Compiler Optimizations
Bayesian Optimization
Autotuning
Spatial Accelerators
Tensor Computations
Code Reproduction
Neural Processing Units
Polyhedral Model
Auto-tuning
Machine Learning Compiler
Neural Network
Program Transformations
Tensor Programs
Deep learning
Tensor Program Optimizer
Search Algorithm
Compiler Infrastructure
Scalalbe and Modular Compiler Systems
Tensor Computation
GPU Task Scheduling
GPU Streams
Tensor Expression Language
Automated Program optimization Framework
AI compiler
memory hierarchy
data locality
tiling fusion
polyhedral model
scheduling
domain-specific architectures
memory intensive
TVM
Sparse Tensor Algebra
Sparse Iteration Spaces
Optimizing Transformations
Tensor Operations
Machine Learning
Model Scoring
AI Compiler
Memory-Intensive Computation
Fusion
Neural Networks
Dataflow
Domain specific Language
Programmable Domain-specific Acclerators
Mapping Space Search
Gradient-based Search
Deep Learning Systems
Systems for Machine Learning
Programming Models
Compilation
Design Space Exploration
Tile Size Optimization
Performance Modeling
High-Performance Tensor Program
Tensor Language Model
Tensor Expression
GPU
Loop Transformations
Vectorization and Parallelization
Hierarchical Classifier
TVM API
Optimizing Compilers
Halide
Pytorch
Optimizing Tensor Programs
Gradient Descent
debug
Automatic Tensor Program Tuning
Operators Fusion
Tensor Program
Cost Model
Weekly Schedule
Spatio-temporal Schedule
tensor compilers
auto-tuning
tensor program optimization
compute schedules
Tensor Compilers
Data Processing Pipeline
Mobile Devices
Layout Transformations
Transformer
Design space exploration
GPU kernel optimization
Compilers
Group Tuning Technique
Tensor Processing Unit
Hardware-software Codeisgn
Data Analysis
Adaptive Systems
Program Auto-tuning
python api
Code Optimization
Distributed Systems
High Performance Computing
code generation
compiler optimization
tensor computation
Instructions Integration
Code rewriting
Tensor Computing
DSL
CodeReproduction
Deep Learning Compiler
Loop Program Analysis
Nested Data Parallelism
Loop Fusion
C++
Machine Learning System
Decision Forest
Optimizfing Compiler
Decision Tree Ensemble
Decision Tree Inference
Parallelization
Optimizing Compiler
decision trees
random forest
machine learning
parallel processing
multithreading
Tree Structure
Performance Model
Code generation
Compiler optimization
Tensor computation
accelerator
neural networks
optimizing compilers
autotuning
performance models
deep neural networks
compilers
auto-scheduling
tensor programs
Tile size optimization
Performance modeling
Program Functionalization
affine transformations
loop optimization
Performance Optimization
Subgraph Similarity
deep learning compiler
Intra- and Inter-Operator Parallelisms
ILP
tile-size
operator fusion
cost model
graph partition
zero-shot tuning
tensor program
kernel orchestration
machine learning compiler
Loop tiling
Locality
Polyhedral compilation
Optimizing Transformation
Sparse Tensors
Asymptotic Analysis
Automatic Scheduling
Data Movement
Optimization
Operation Fusion
Compute-Intensive
Automatic Exploration
data reuse
deep reuse
Tensorize
docker
graph substitution
compiler
Just-in-time compiler
graph
Tensor program
construction tensor compilation
graph traversal
Markov analysis
Deep Learning Compilation
Tensor Program Auto-Tuning
Decision Tree
Search-based code generation
Domain specific lanuages
Parallel architectures
Dynamic neural network
mobile device
spatial accelerate
software mapping
reinforcement learning
Computation Graph
Graph Scheduling and Transformation
Graph-level Optimization
Operator-level Optimization
Partitioning Algorithms
IR Design
Parallel programming languages
Software performance
Digitial signal processing
Retargetable compilers
Equational logic and rewriting
Tensor-level Memory Management
Code Generation and Optimizations
Scheduling
Sparse Tensor
Auto-Scheduling
Tensor
Coarse-Grained Reconfigurable Architecture
Graph Neural Network
Reinforcement Learning
Auto-Tuning
Domain-Specific Accelerator
Deep learning compiler
Long context
Memory optimization
code analysis
transformer
architecture-mapping
DRAM-PIM
LLM