Current solutions
Existing frameworks optimize tensor programs by applying fully equivalent transformations
The author’s proposal
optimize tensor programs by exploiting partially equivalent transformations
面临的挑战
(1) examining equivalence and correction kernels - (为什么部分等价变换会影响模型的准确度)
(2) design space is substantially enlarged
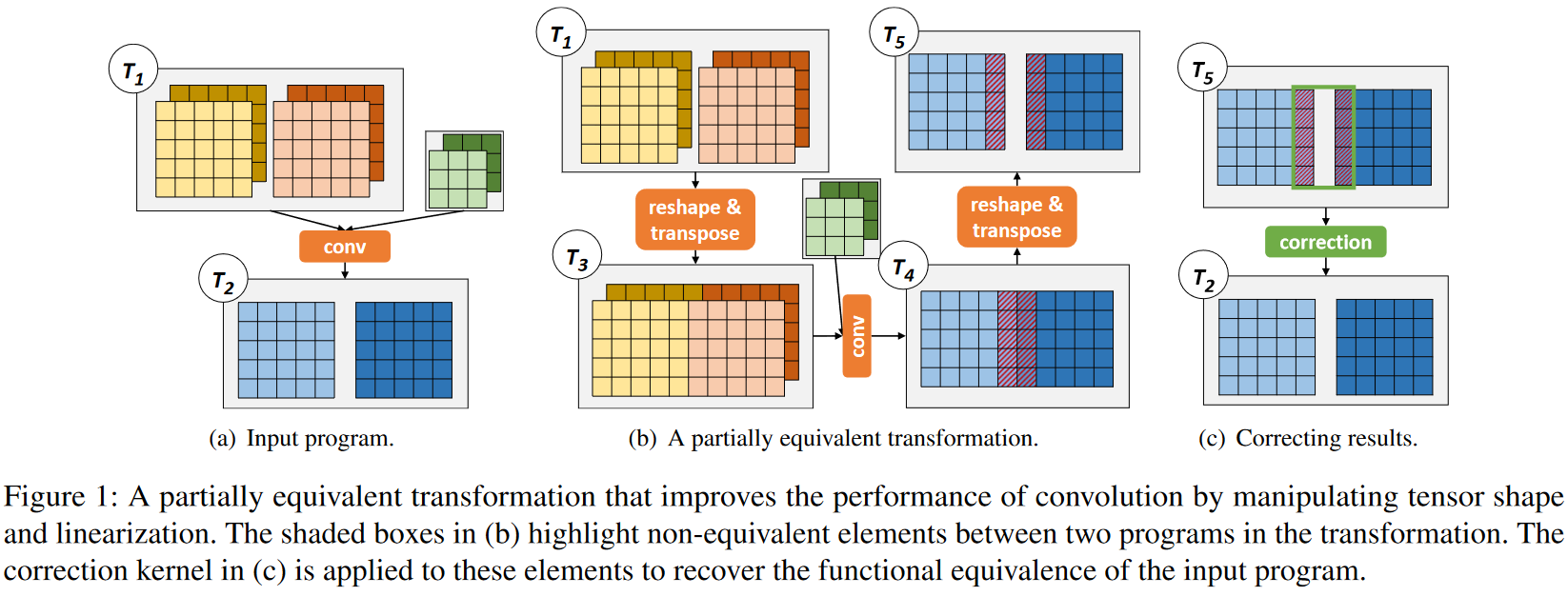
partially equivalent transformations
- change the shape and linearization of its tensors-GPU并行性优化、内存访问优化、计算效率
- replace less efficient operators with more optimized ones with similar semantics
- modify the graph structure of a tensor program to enable additional optimizations
Fully equivalent transformations:转换前后的程序对于任意输入都产生完全相同的输出结果
Partially equivalent transformations:转换后的程序只在输出张量的部分区域保持等价性
Design
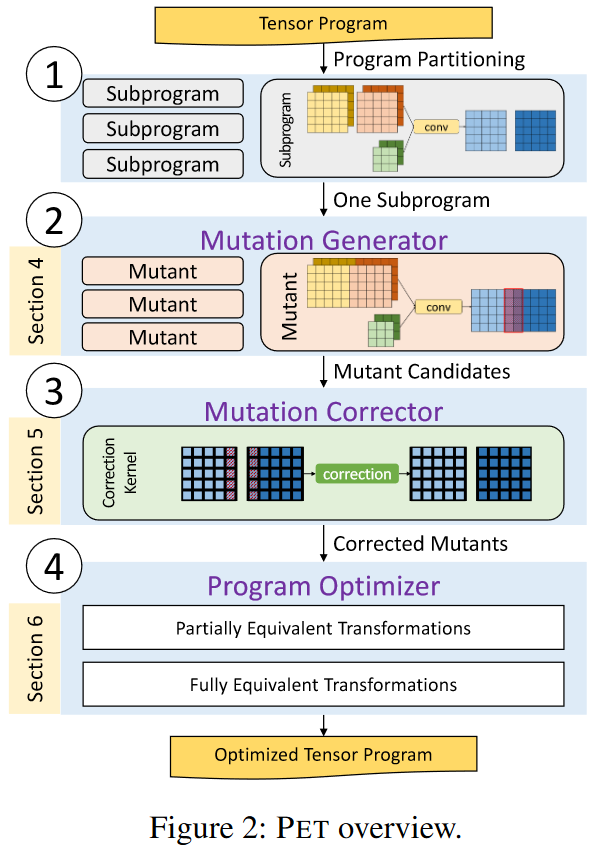
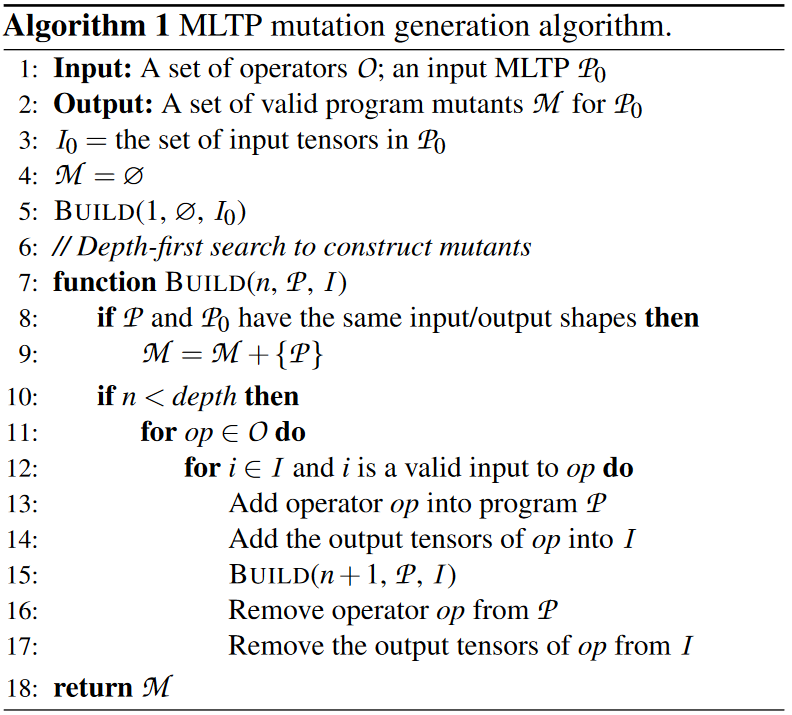
Mutation Generator
Mutation Generation Algorithm
Mutation Corrector
- 输出的算子可能十分大,对于算子的每个元素检查是不行的
- 每个输出的元素的验证可能取决于张量运算符中的大量输入变量
Theoretical Foundations
Theorem 1
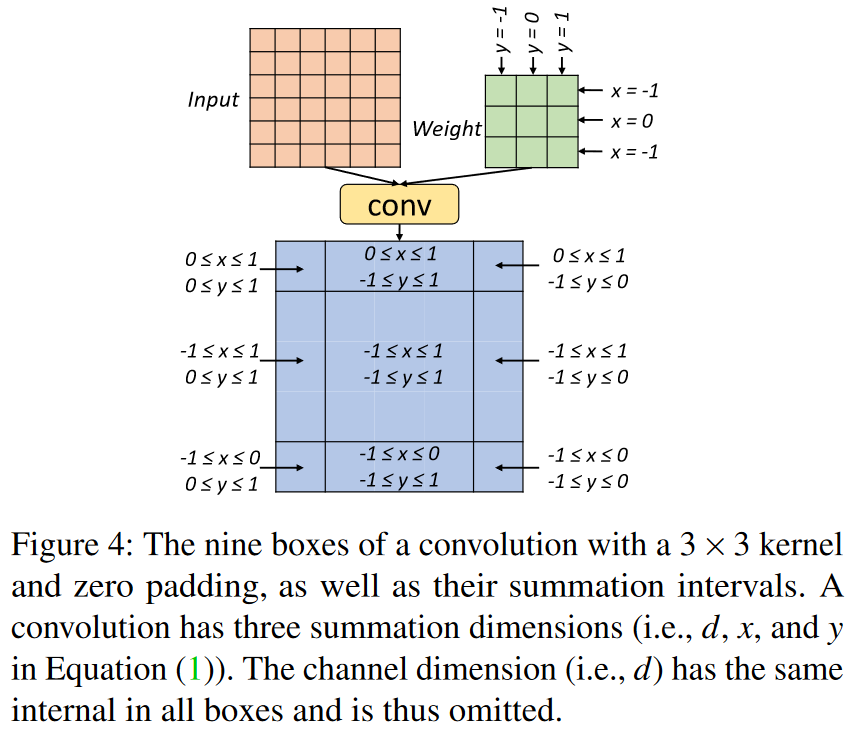
box:输出张量中具有相同求和区间的区域,例如上图展示3*3卷积的9个不同的box 定理1的核心思想:如果两个程序在box内的m+1个特定位置等价,那么它们在整个box区域都等价,从而减少验证工作量
Theorem 2

定理2的核心思想:使用随机测试来验证等价性,如果两个程序不等价,用随机输入测试能以很高概率发现,不需要穷举所有可能的输入
Mutation Correction Algorithm
- Box propagation
- Random testing for each box pair
- Correction kernel generation
Program Optimizer
Program Splitting
分割策略:在非线性算子处进行分割(非线性算子在神经网络中的分布、PET只支持多线性张量程序)
Subprogram Optimization

Post-Optimizations
- Inverse elimination
- Operator fusion
- Preprocessing
Evaluation
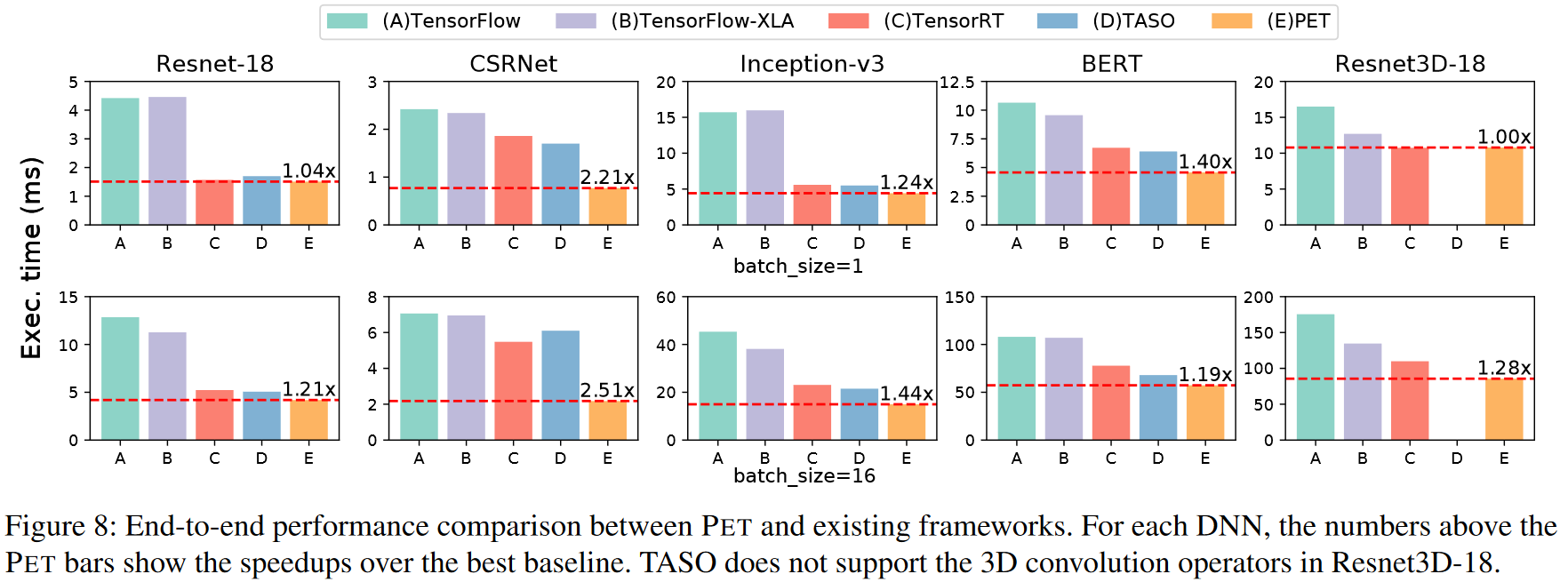
Thinking
(1) 搜索策略:使用简单的深度优先搜索来生成变体,是否可以用其他
(2) 算子优化:只针对线性算子,非线性算子优化是否也需要非等价转换
(3) 硬件优化:优化主要针对GPU,没有考虑不同硬件架构的特点,像TVM可以扩展各硬件平台上
(4) 自动化程序:一些参数需要手动调整,缺乏自适应优化机制
后续计划:需了解一些GPU上张量计算相关方面的知识
Reference
PET: Optimizing Tensor Programs with Partially Equivalent Transformations and Automated Corrections