Motivation
with tensor-oriented data analytics is how to design a high-performance library for various tensor algorithms on heterogeneous systems
面临的挑战:
(1) 不同的调度原语组合会导致不同性能
(2) 不同的硬件也会增加复杂性
Overview
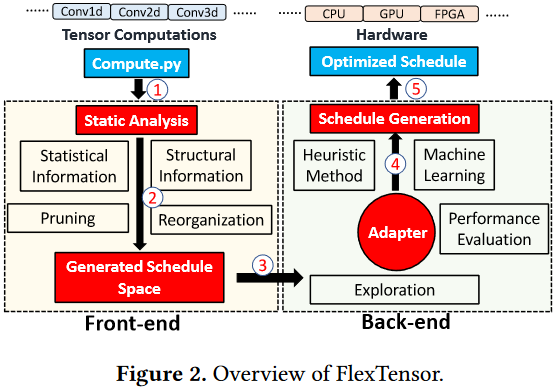
Front-end Analysis and Schedule Space
Static Analysis:
$O[i_1, i_2, \ldots, i_M] = \mathcal{F}(I_1, I_2, \ldots, I_N)$
spatial loops: the loops without data dependency
reduce loops: the lossp have data dependency and usually run in serial
statistical information $\rightarrow$ graph nodes (number of spatial loops and reduce loops、trip counts of spatial loops and reduce loops、loop orders)
structural information $\rightarrow$ graph edges (number of nodes in mini-graph、number of input tensors and output tensors of each node、number of consumer nodes of each node)
Schedule Space Generation
prue the design space by deleting the points that are unlikely to lead to good performance
- limit the depth of primitives combination
- prune the parameter space
- pre-determine certain decisions for different hardware
rearrange the space by exploiting structural similarity
- 将一维列表重组为高维空间
- 相邻点具有相似结构
- 有助于后续探索局部局域
Back-end Exploration and Optimization
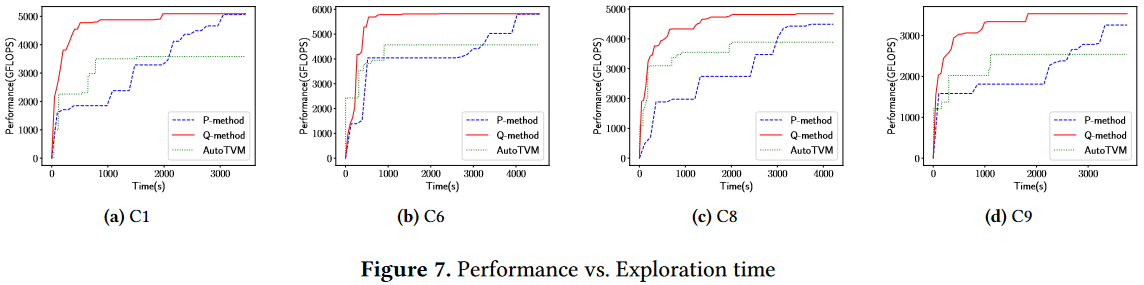
Exploration with Heuristics and Machine learning:
(1) which point in H is selected as the starting point for the next step (heuristic method)
(2) given the starting point p, which direction d to move along to get a new point in G (machine learning method)
针对第一个问题使用启发式方法(基于模拟退火)
def select_next_point(points, best_performance):
for p in points:
prob = exp(-γ * (best_performance - p.performance) / best_performance)
if random() < prob:
return p
针对第二个问题使用机器学习方法(基于Q-learning)
def explore_schedule_space():
H = set() #已评估点集合
while not done:
p = heuristic_select_point(H) # 使用启发式方法选择起始点
d = q_network.predict_best_direction(p) # 使用Q-learning选择移动方向
new_p = move_to_direction(p, d) # 获取新点并评估
performance = evaluate(new_p)
H.add(new_p) # 更新集合
Q-learning训练过程
def train_q_network():
main_network = Network()
target_network = Network()
for (p, e, reward) in collected_data:
target = α * max(target_network.predict(e)) + reward
loss = (main_network.predict(p) - target)² # 训练主网络
main_network.update(loss)
if steps % update_frequency == 0: # 定期更新目标网络
target_network.weights = main_network.weights
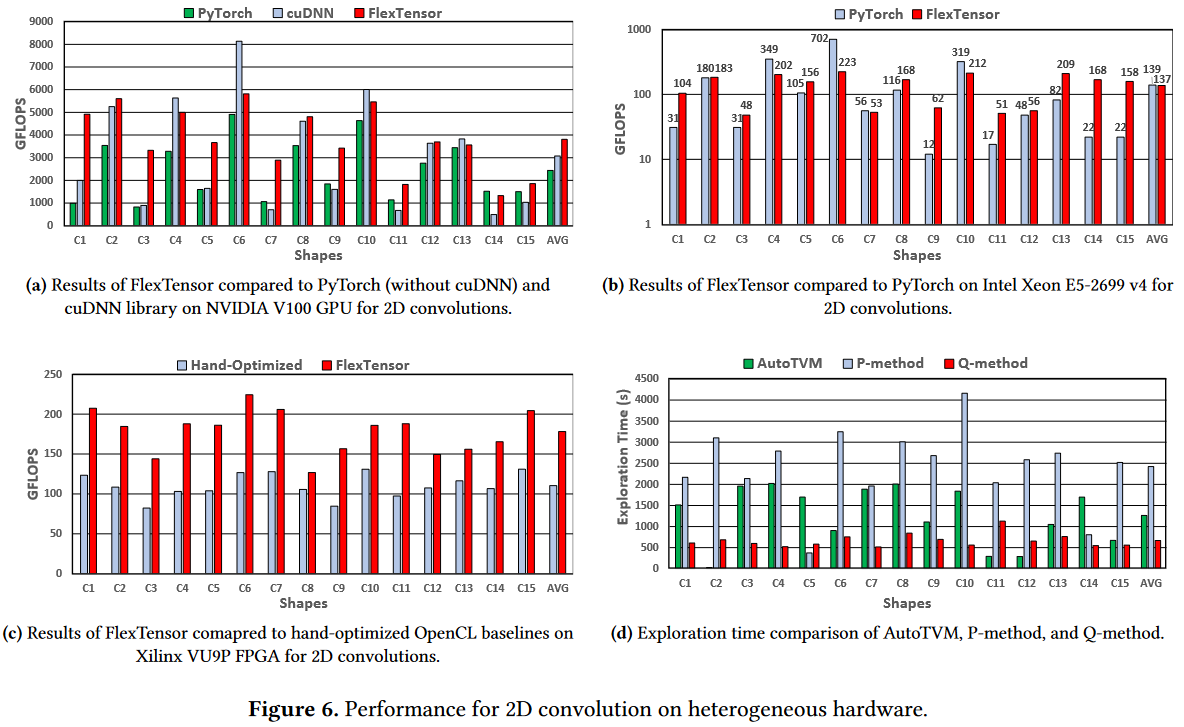
Performance Comparison
Optimized Schedule Implementation:
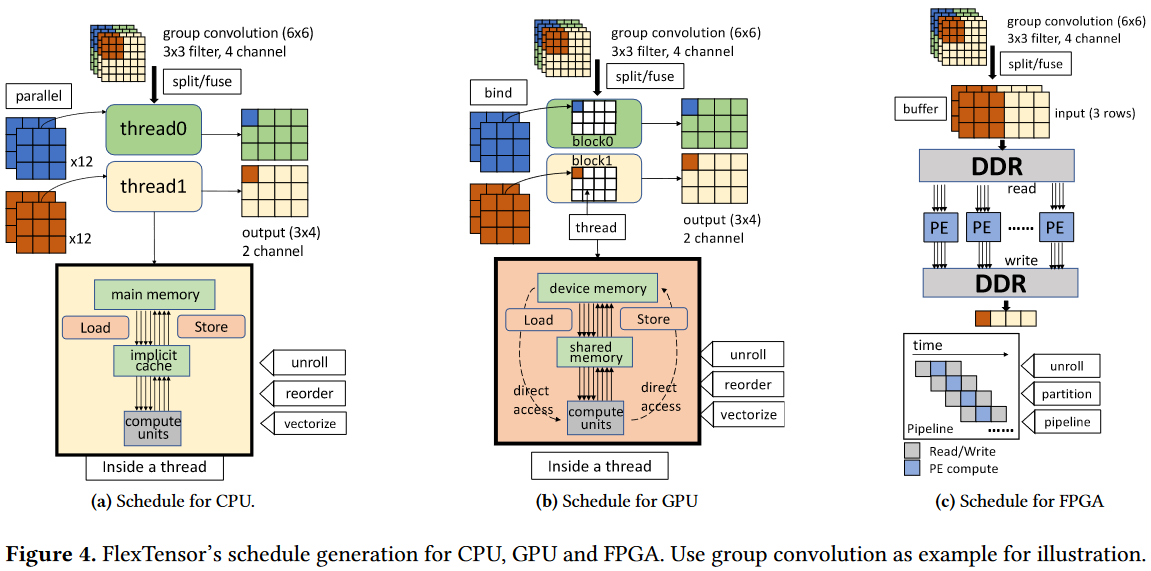
Evaluation
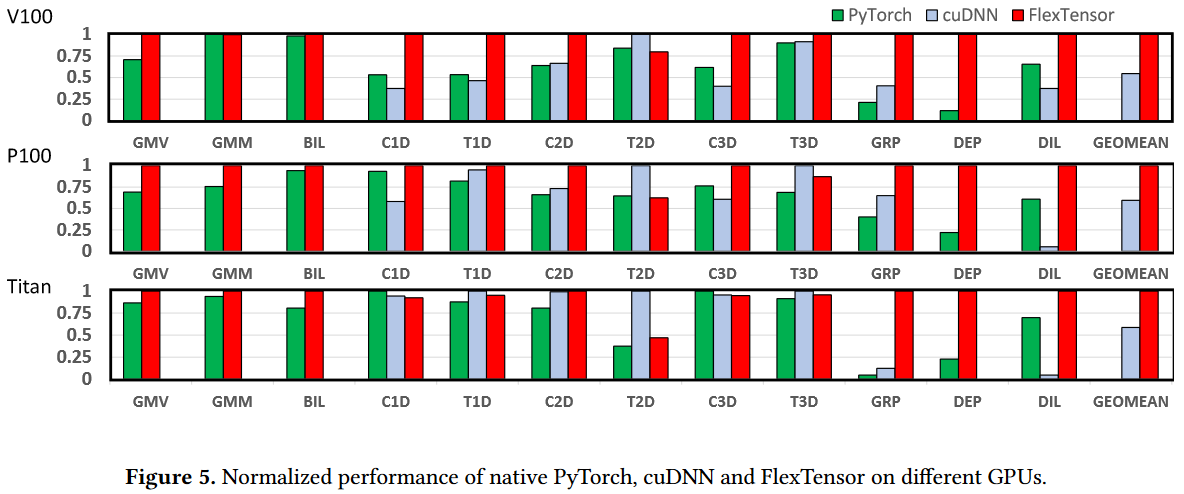
Overall Speedups on GPUs